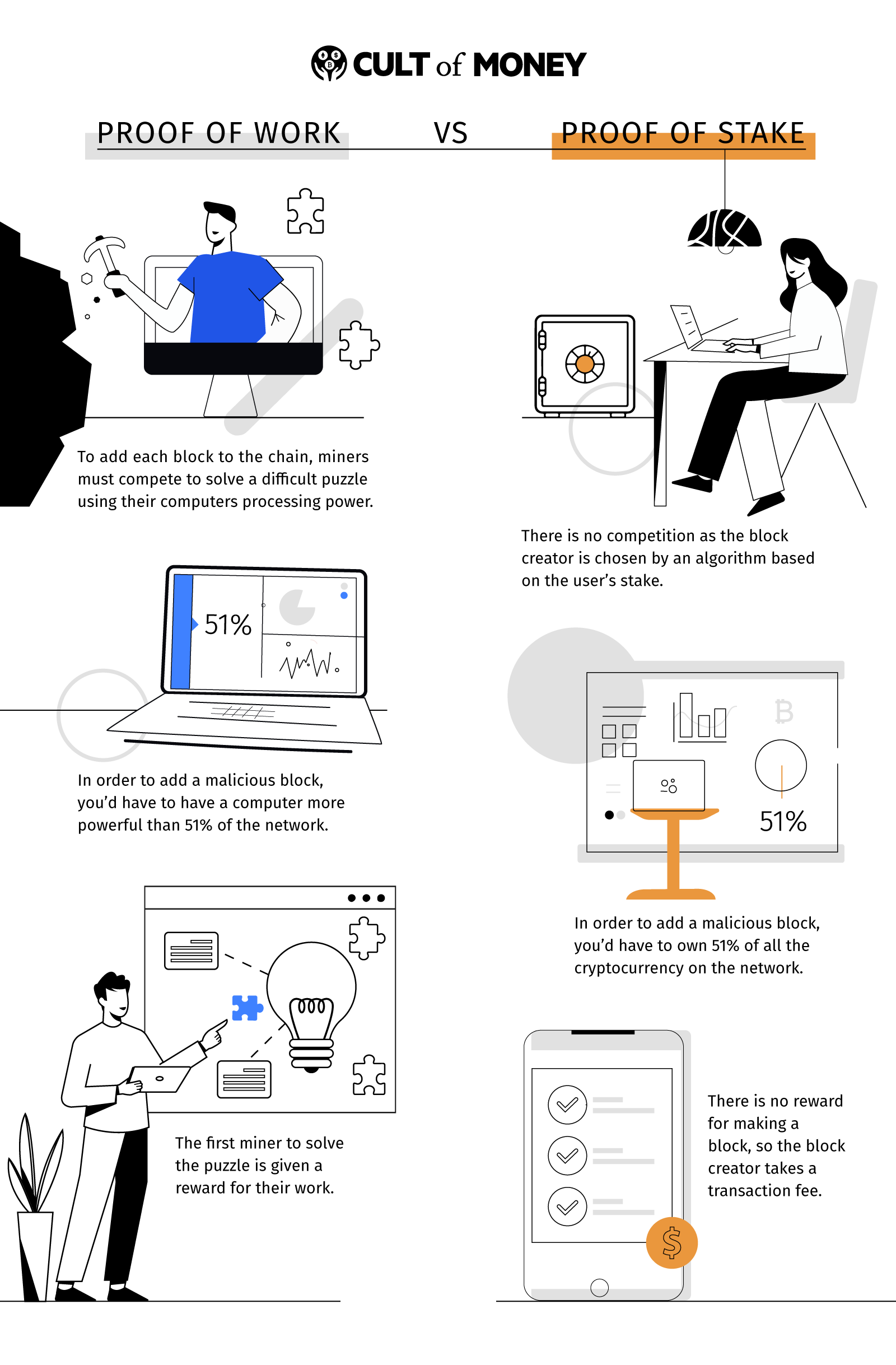
Once you start diving down the crypto rabbit hole, you’re inevitably going to hear terms like Proof-of-Work (PoW), Proof-of-Stake (PoS), and Proof-of-History (PoH).
For new investors, this might sound like complex jargon you don’t need to know. However, these protocols are essential for how popular cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum function. In fact, it’s these protocols that verify blockchain transactions without the need of a third-party, helping crypto stay decentralized.
Ultimately, the more you understand about the differences between PoW vs. PoS vs. PoH, the better. Cryptocurrency is an emerging asset class with incredible opportunities. But it’s critical to understand the technology behind the scenes so you can make informed investing decisions.
What Are Consensus Mechanisms?
Consensus mechanisms, also known as consensus algorithms, are how the nodes in a network agree on which blockchain transactions are valid.
Remember, a blockchain is basically a digital ledger of information that’s distributed to everyone in the network. This means every node has an identical picture of the state of the blockchain and previous transactions. To update this ledger and keep it universally identical, nodes in the network have to agree on which new blocks are valid and should be added to the chain.
To reach consensus, at least 51% of the nodes on a network have to agree that a block is valid and should be added.
This is the simple explanation of what consensus mechanisms are and how they’re used in cryptocurrency. However, different cryptocurrencies have different consensus mechanisms, and this has drastic implications for energy usage, security, and scalability.
What Is Proof-Of-Work (PoW)?
Proof-of-Work is likely what most beginner cryptocurrency investors are familiar with as it’s the consensus mechanism Bitcoin and Ethereum use. It’s also the mechanism that’s at play when you hear people talk about Ethereum and Bitcoin mining.
How Does PoW Work?
With Proof-of-Work, blocks with transactions have to be verified by network participants before being added to the chain. In order to verify blocks, validators use computing power to solve complex cryptographic puzzles. When a participant successfully validates a block, that block is added to the chain and the participant receives Bitcoin as a reward.
This process of solving complex problems with computing power in exchange for block rewards is what mining is. In Bitcoin’s case, mining rewards for completing a block halves every four years or so as the total amount of circulating BTC increases. Currently, miners get 6.25 BTC for successfully validating a block.
Proof-of-Work is very energy intensive. The amount of computing power that’s mining for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, known as hash rate, is immense. This results in more energy expenditure around the world. It’s also impacted the global GPU market as miners buy expensive computer hardware to mine more efficiently.
Energy consumption is one downside of Proof-of-Work. Additionally, PoW follows a “longest chain” rule in which the longest chain in a blockchain is accepted by users as being valid. This means that PoW cryptos are more susceptible to 51% attacks, which occurs when an entity achieves 51% of total hash rate and builds the longest chain with fraudulent blocks and double-spends their crypto.
Finally, PoW has been criticized for lacking scalability. For example, Bitcoin miners validate blocks every 10 minutes on average, while PoS and PoH validate transactions much faster. It’s clear why Bitcoin and Ethereum aren’t ideal for making tons of daily transactions, especially when you consider costs like ETH gas fees.
Advantages & Disadvantages Of Proof-Of-Work (PoW)
What Is Proof-Of-Stake (PoS)?
Proof-of-Stake is the main alternative to Proof-of-Work and is the consensus mechanism that cryptocurrencies like Algorand, Cardano, Solana, and Tezos use to validate transactions.
Ethereum is also switching from PoW to PoS in its Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, which aims to improve scalability and security.
How Does PoS Work?
With Proof-of-Stake, stakers are like cryptocurrency miners, except stakers lock up cryptocurrency they own to act as validator nodes. The likelihood of validating a new block and earning block rewards depends on how much cryptocurrency you’re staking. This means that the more cryptocurrency you hold and stake, the higher chance you have to be selected as the one to validate a block.
The main difference between Proof-of-Stake and Proof-of-Work is that PoS doesn’t require nearly as much energy to validate blocks. This is because stakers lock funds using smart contracts and don’t have to use mining to solve energy-intensive cryptographic problems.
PoS is also more scalable than PoW because PoS allows for more transactions per second (TPS). While it takes around 10 minutes to validate a single Bitcoin transaction, Cardano has a TPS of around 257. And Vitalik Buterin, the founder of Ethereum, believes the ETH 2.0 upgrade will facilitate up to 100,000 TPS for ETH.
Finally, you can make the argument that PoS is a fairer consensus mechanism because it truly rewards stakeholders. With PoW, large entities dominate large percentages of hash rates, and it’s expensive to get into mining. But with PoS, even beginner investors can stake their cryptocurrency independently or through staking pools to earn rewards.
Furthermore, PoS acts as an additional layer of security because you need skin in the game. The odds of a 51% attack occurring on a PoS cryptocurrency isn’t likely for established coins. This is because the attacker would have to own 51% of the cryptocurrency that’s being staked. Not only is this extremely expensive, but it’s counterproductive to attack a cryptocurrency and potentially lower its price when you’re a significant stakeholder.
Advantages & Disadvantages Of Proof-Of-Stake (PoS)
What Is Proof-Of-History (PoH)?
Proof-of-History is a consensus mechanism that Solana, one of the largest cryptocurrencies by market cap, uses alongside PoS to help solve the issue of universal blockchain time and increase network speed.
Solana’s advantage is that it’s extremely efficient. It can process transactions much faster than cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum due to using PoH and other innovations.
How Does PoH Work?
In Solana’s whitepaper, founder Anatoly Yakovenko explains how PoH aims to create a ledger with a verifiable clock so nodes in the network know the recorded passage of time without having to rely on other nodes.
In a nutshell, with PoH, nodes have their own internal clock that verifies events and the passage of time. The proof uses a verifiable delay function (VDF) to hash incoming events and also notes when events occurred. When other nodes look at the sequence of hashes, they can immediately tell the order in which events occurred without having to validate time with other nodes.
PoH can be extremely confusing to read up on since a lot of the writers who discuss it are engineers/coders/crytographers. But the video below from Solana itself is a short and snappy explainer that can help anyone to gain a better grasp of how PoH works:
Solana also has several other technological innovations to improve efficiency. For example, it uses the Turbine protocol which condenses data into smaller sizes to lower bandwidth requirements and increase TPS. It also uses Sealevel, which lets smart contracts run in parallel.
Thanks to all of these improvements, Solana states it can achieve over 60,000 TPS. Fast transaction speeds and incredibly low fees are why Solana is often called the “Ethereum killer” by its advocates.
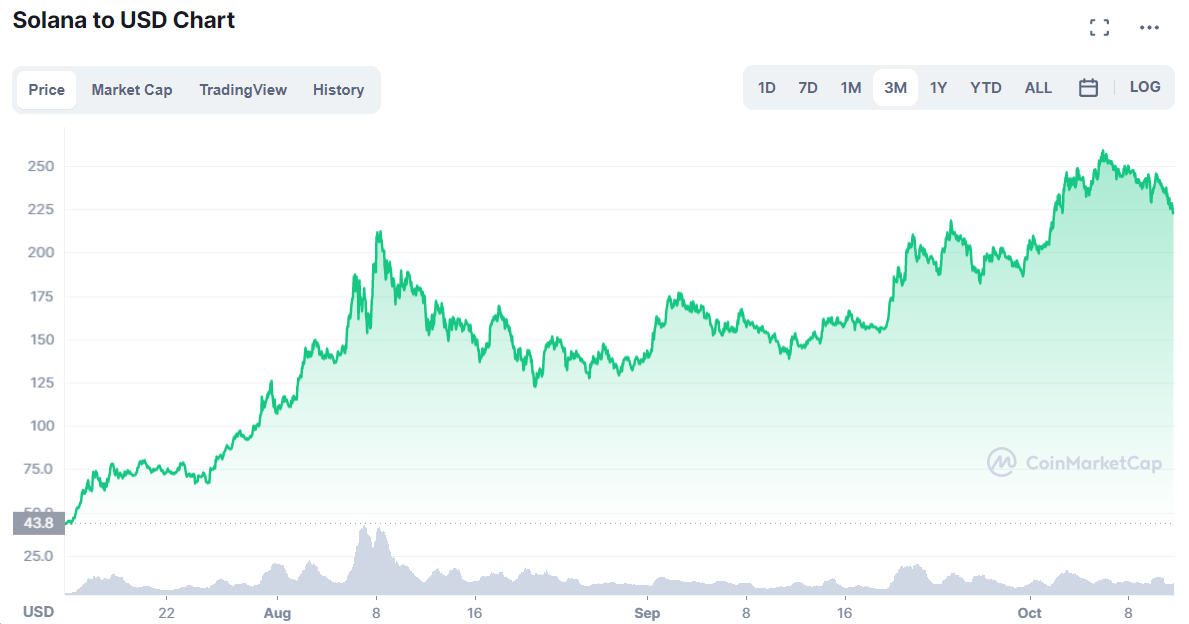
But despite Solana’s efficiency, there have been bumps along the way. On September 14th, 2021, Solana’s network crashed and was offline for 17 hours. The crash was caused by a bot attack that essentially flooded the network with over 400,000 transactions per second, causing validators to crash and stall the network.
This crash led to Solana losing approximately $20 billion in market cap. Granted, Solana’s price has since recovered, but it highlights the fact that Solana is still in its infancy and could experience more growing pains.
Advantages & Disadvantages Of Proof-Of-History (PoH)
What Does All This Mean For Investors?
Terms like Proof-of-Work, Proof-of-Stake, and Proof-of-History might seem like pure jargon. But with any asset class, it’s important to understand what you’re actually investing in and why it might be valuable in the first place. For cryptocurrency, this means understanding the fundamental technology behind different projects.
Furthermore, innovations like PoS and PoH create new opportunities besides just buying cryptocurrency on an exchange. For example, with staking, you can earn passive rewards with your cryptocurrency. You can also investigate lending-based platforms like BlockFi and Celsius, which let you deposit your cryptocurrency to earn interest.
Ultimately, Proof-of-Work and Bitcoin laid the groundwork for cryptocurrency consensus mechanisms. But the space continues to develop rapidly and investors should at least take into a consideration the long-term viability of a coin's validation technology before choosing to invest.

Tom Blake is a personal finance writer with a passion for making money online, cryptocurrency and NFTs, investing, and the gig economy.